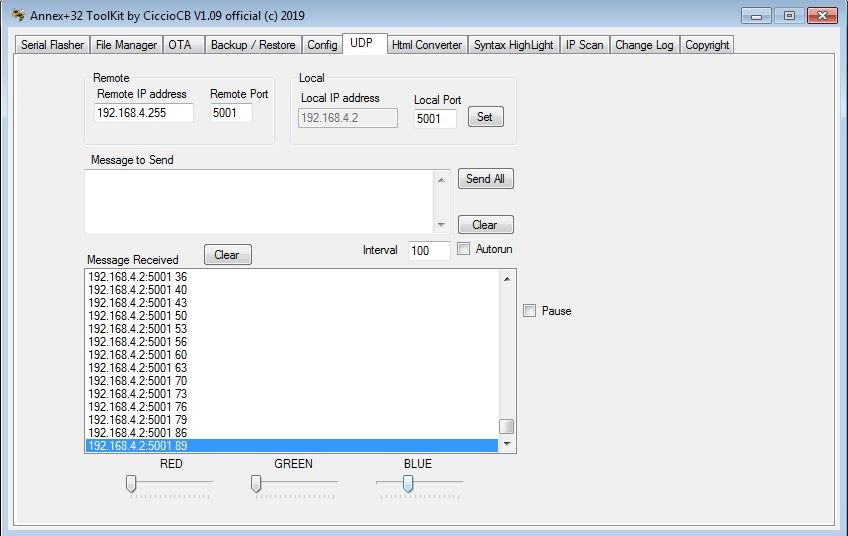
The Red, Green, Blue LEDs of a Sonoff B1 Lamp or neopixels or a standard RGB LED can be controlled by broadcasting the individual R, G, B values OR a single 24bit combined RGB value using UDP .
At the bottom of the Annex Toolkit UDP Console tab are 3 sliders which broadcasts a 24bit combined RGB value to the subnet.
These sliders can be used as a UDP RGB lamp controller for the simple scripts below.
Don't let the relative simplicity fool you... running the same simple
script on multiple devices offers impressive
synchronized lighting control.
This first script is for a Sonoff B1 Lamp: view Sonoff B1 demo vid
Basic:
'Simple UDP Sonoff B1 Lamp Controller - developed on Annex 1.41 beta2 - Electroguard sonoffb1.init sonoffb1.rgb 0 'RGB leds OFF udp.begin(5001) 'change port number if wished, but must match with Toolkit UDP Console port setting onudp udpRX wait udpRX: sonoffb1.rgb val(udp.read$) return '----------- End ------------ Using the 3 R,G,B sliders is pretty cool, but If you're into home automation then you'll probably love what's coming next... Notice towards the end of the demo that the RGB LEDs can also be
controlled simply by sending a value from the 'Message to Send' window. Type in 0 then click 'Send all' to turn it off. Similarly send &h00ff for green, &hff0000 for red, &hffffff for white, and send 0 whenever you wish to turn all LEDs off. Any
Annex devices are capable of sending such UDP broadcasts, so it is very
easy for Annex to control simple home-automation lighting. Using different UDP ports on the same subnet allows having multiple independent lighting channels A noticeable difference from the previous script is that the incoming 24bit combined RGB value needs to be spilt into its 3 R,G,B component values to operate the appropriate PWM pins. Also, the 0 to 255 UDP slider values need multiplying by 4 to match the 0 to 1023 PWM range.,
Basic:
'Simple UDP RGB LED Controller - developed on Annex 1.41 beta2 - Electroguard Rpin=12: Gpin=15: Bpin=13 'assign gpio pins to R,G,B leds r=0: g=0: b=0 'assign initial r,g,b values gosub changeit 'branch to set values udp.begin(5001) onudp udpRX wait udpRX: x=val(udp.read$) 'read incoming 24bit combined RGB value b=(x and &hff) 'extract just the B value g=(x >> 8) and &hff 'extract just the G value r=(x >> 16) and &hff 'extract just the R value gosub changeit return changeit: pwm(Rpin)=r*4 'multipy the 0 to 255 r,g,b values by 4 to match the 0 to 1023 PWM range pwm(Gpin)=g*4 pwm(Bpin)=b*4 return '----------- End ------------
Basic:
'Simple UDP Neopixels Controller - developed on Annex 1.41 beta2 - Electroguard neo.setup 12 'number of neopixels, example is for a 12 pixel ring, (Data In connected to gpio2) neo.strip 0,11,0 'neopixels off udp.begin(5001) 'change port number if wished, but must match with Toolkit UDP Console port setting onudp udpRX wait udpRX: neo.strip 0,11, val(udp.read$) return '----------- End ------------ |
|
|